Sim2Real Rope Cutting with a Surgical Robot Using Vision-based Reinforcement Learning
Mustafa Haiderbhai, Radian Gondokaryono, Andrew Wu, Lueder A. Kahrs
Medical Computer Vision and Robotics Lab, University of Toronto
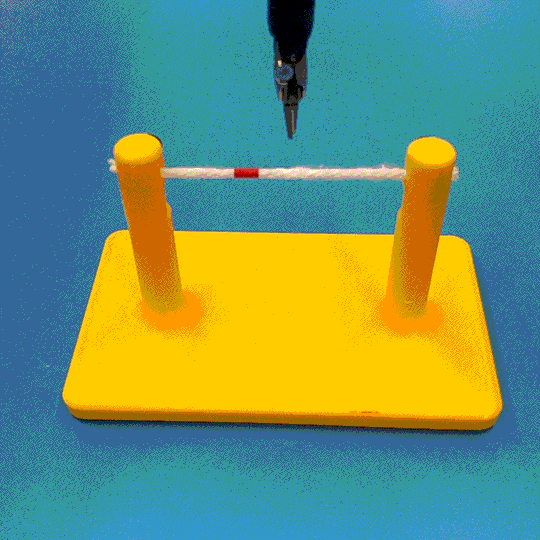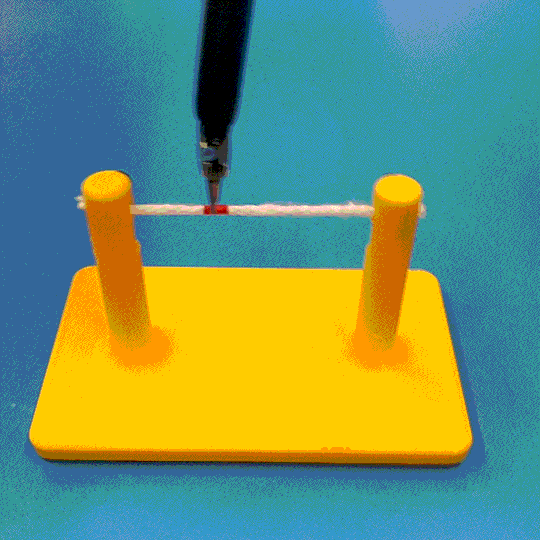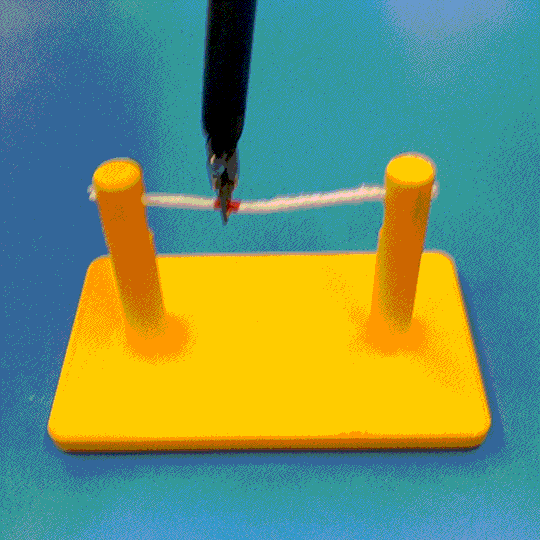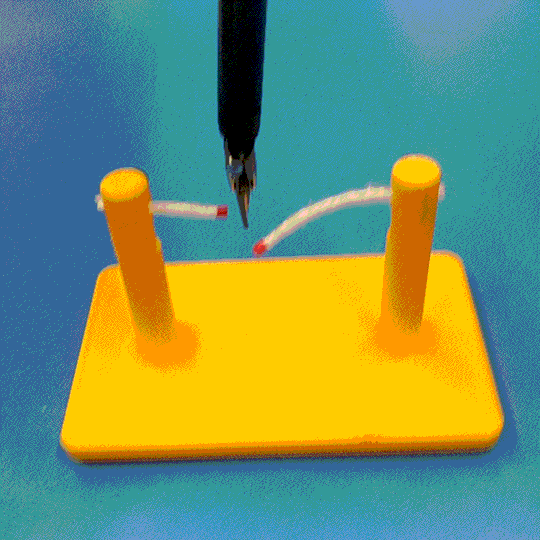
Abstract
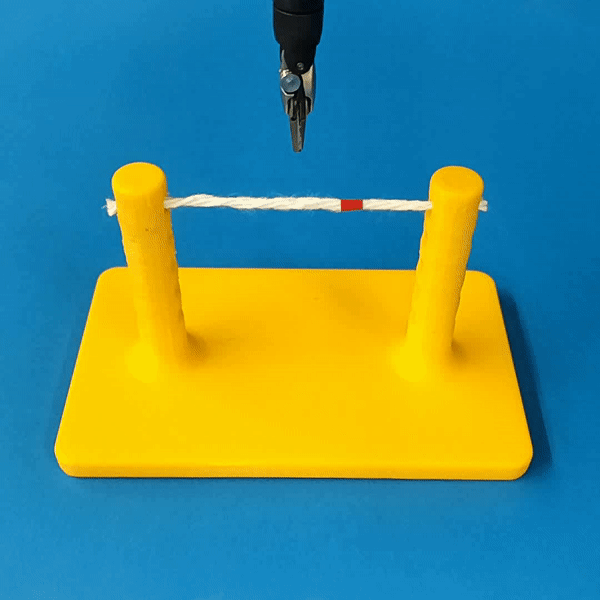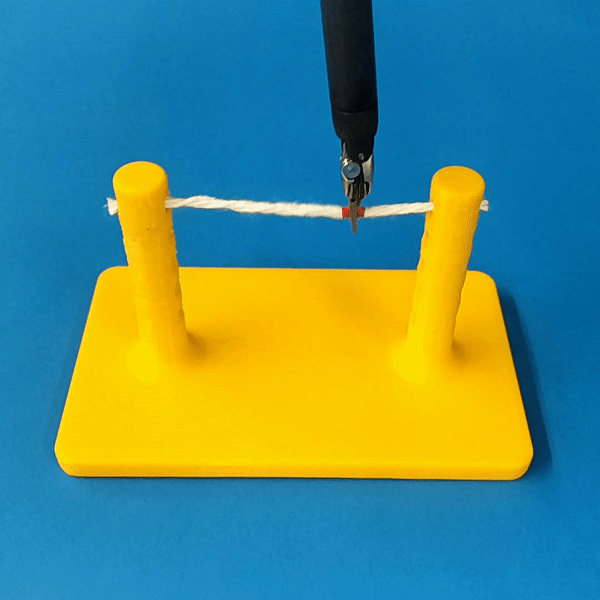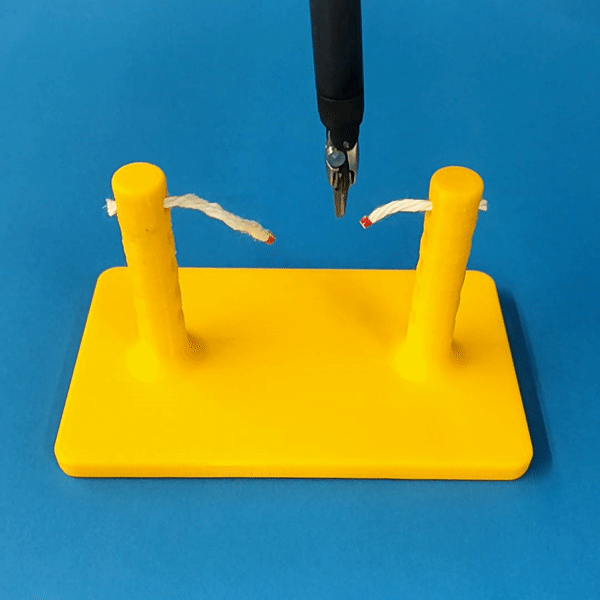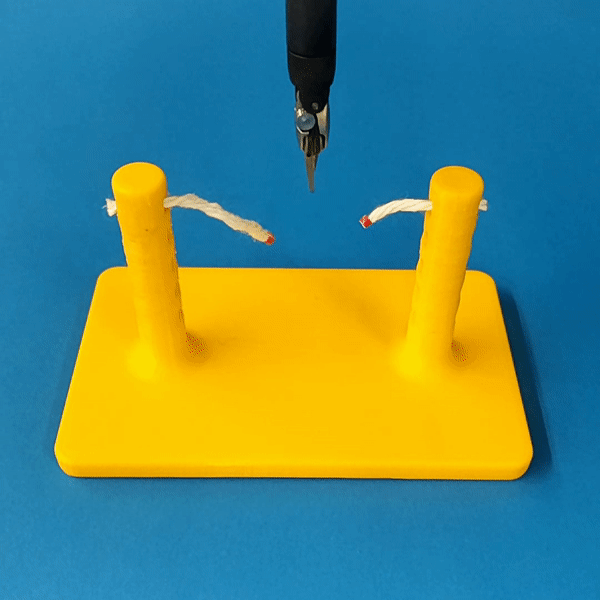
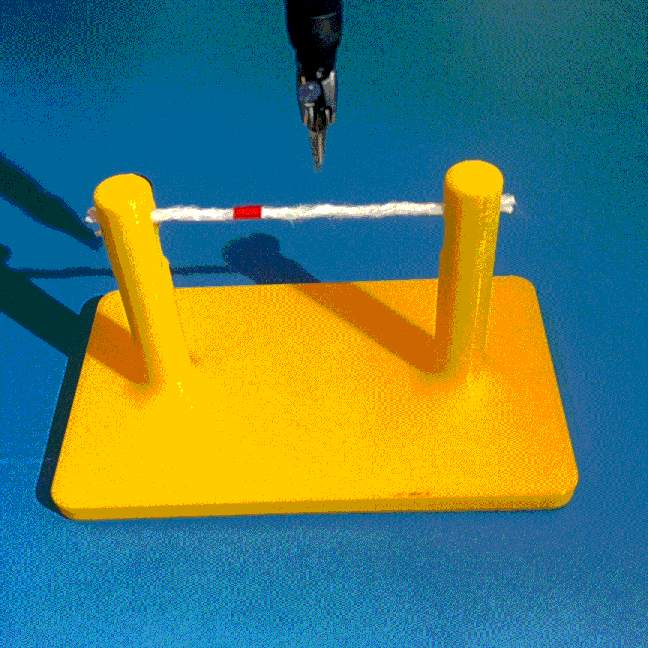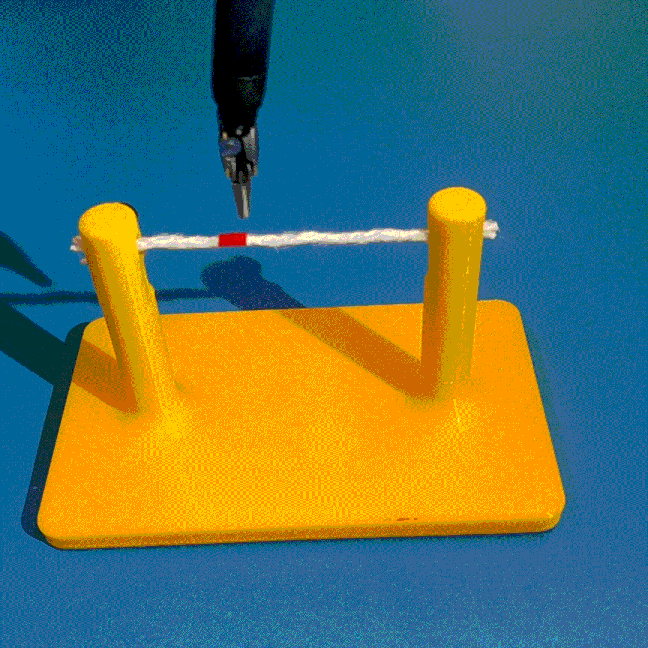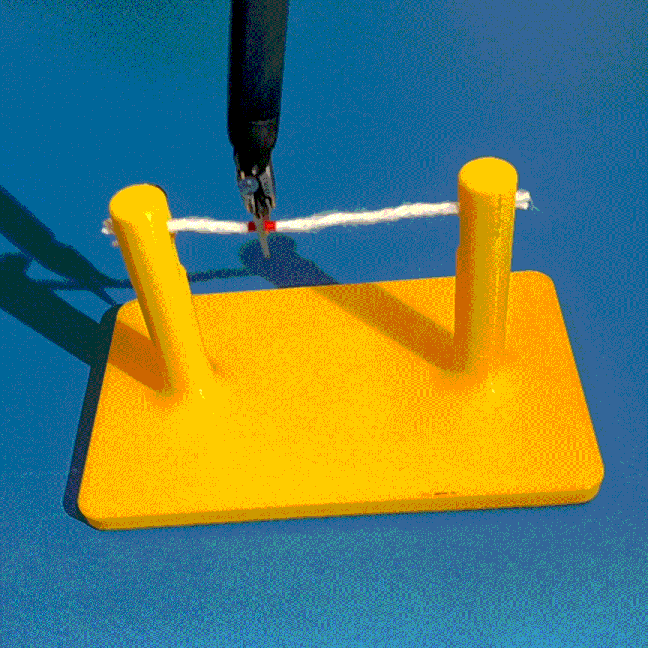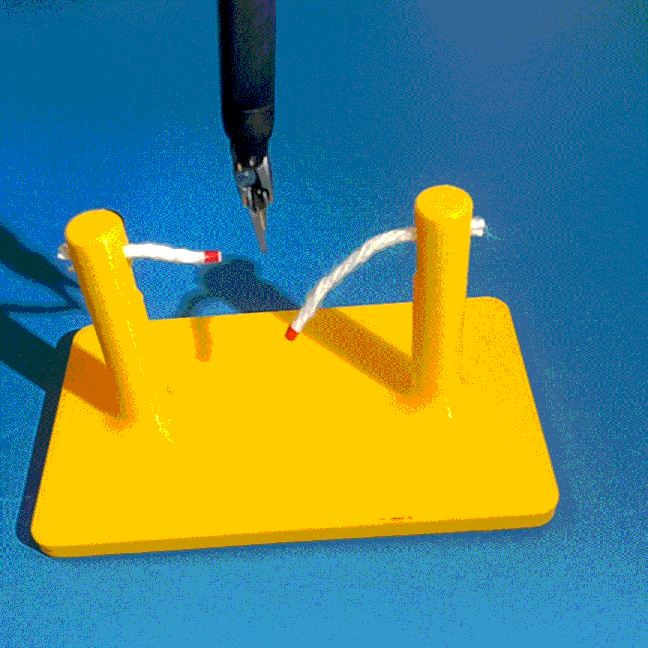
Cutting is a challenging area in the field of autonomous robotics but is especially interesting for applications such as surgery. One large challenge is the lack of simulations for cutting with surgical robots that can transfer to the real robot. In this work, we create a surgical robotic simulation of rope cutting with realistic visual and physics behavior using the da Vinci Research Kit (dVRK). We learn a cutting policy purely from simulation and sim2real transfer our learned models to real experiments by leveraging Domain Randomization. We find that cutting with surgical instruments such as the EndoWrist Round Tip Scissors comes with certain challenges such as deformations, cutting forces along the jaw, fine positioning, and tool occlusion. We overcome these challenges by designing a reward function that promotes successful cutting behavior through fine positioning of the jaws directly from image inputs. Policies are transferred using a custom sim2real pipeline based on a modular teleoperation framework for identical execution in simulation and the real robot. We achieve a 97.5% success rate in real cutting experiments with our 2D model and a 90% success rate in 3D after the sim2real transfer of our model. We showcase the need for Domain Randomization and a specialized reward function to achieve successful cutting behavior across different material conditions through optimal fine positioning. Our experiments cover varying rope thicknesses and tension levels and show that our final policy can successfully cut the rope across different scenarios by learning entirely from our simulation
Cutting is Challenging
Cutting is a challenging task for autonomous robotics due to topological change and deformations. Simulations play a key role in learning autonomous agents but simulations for surgical robotic cutting is an open challenge.
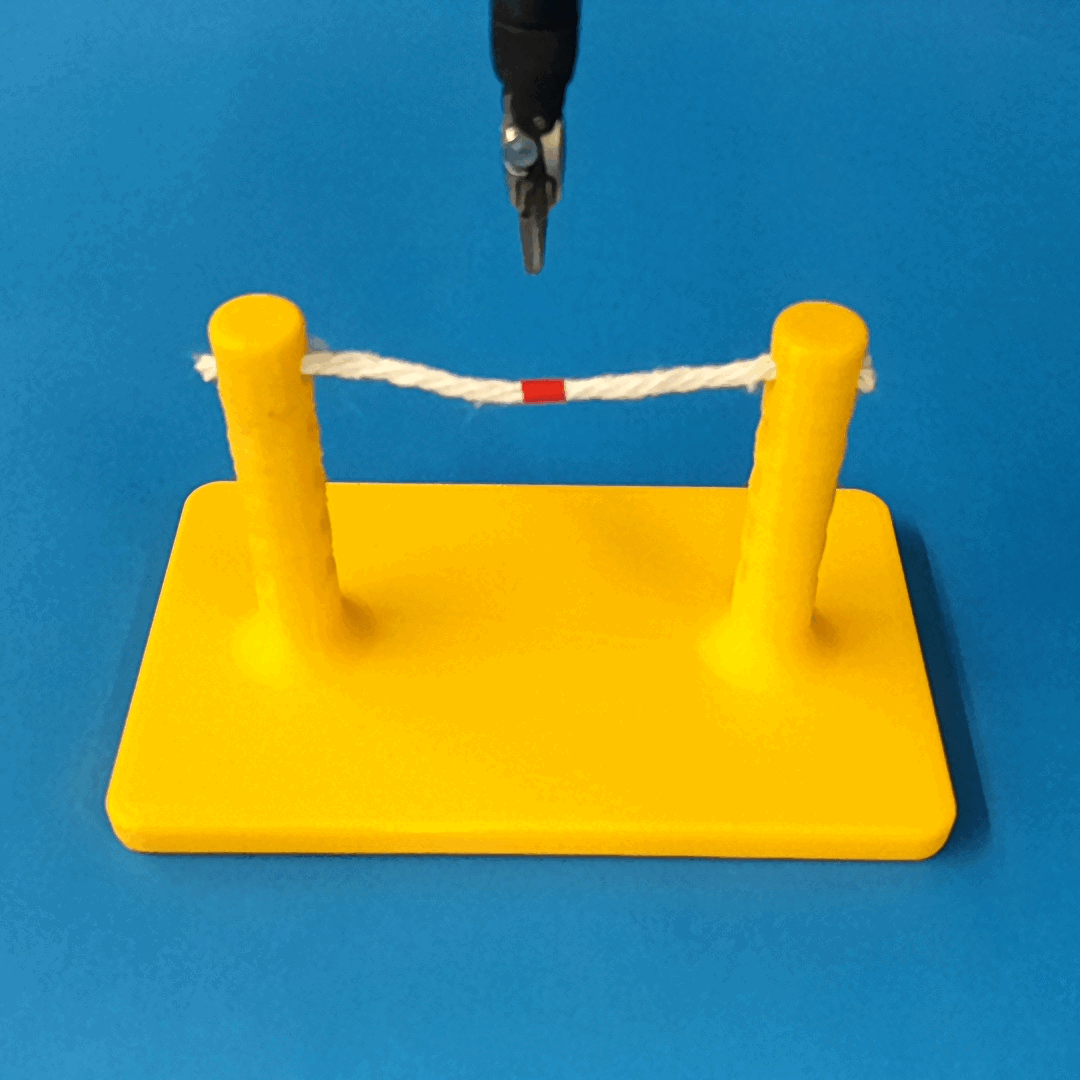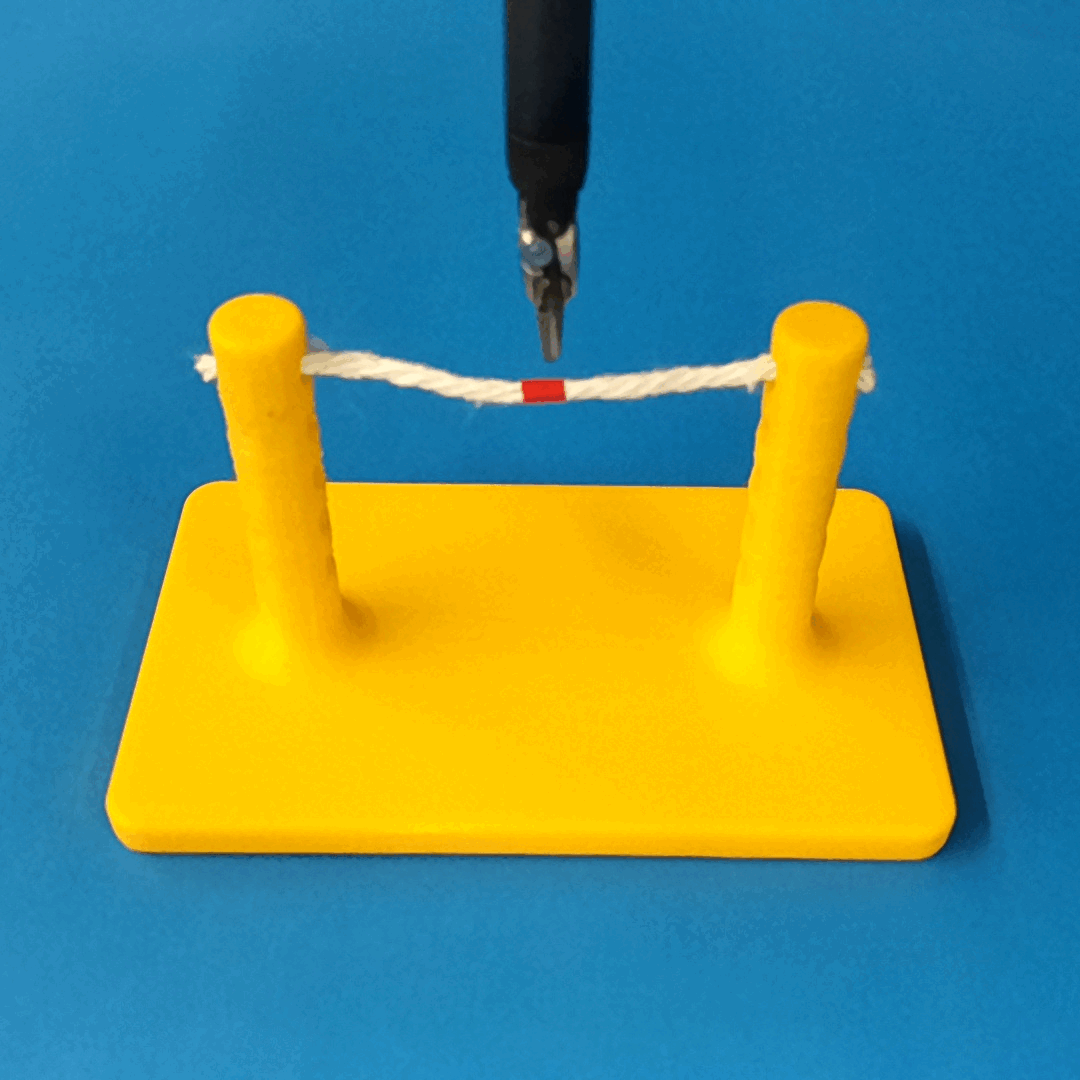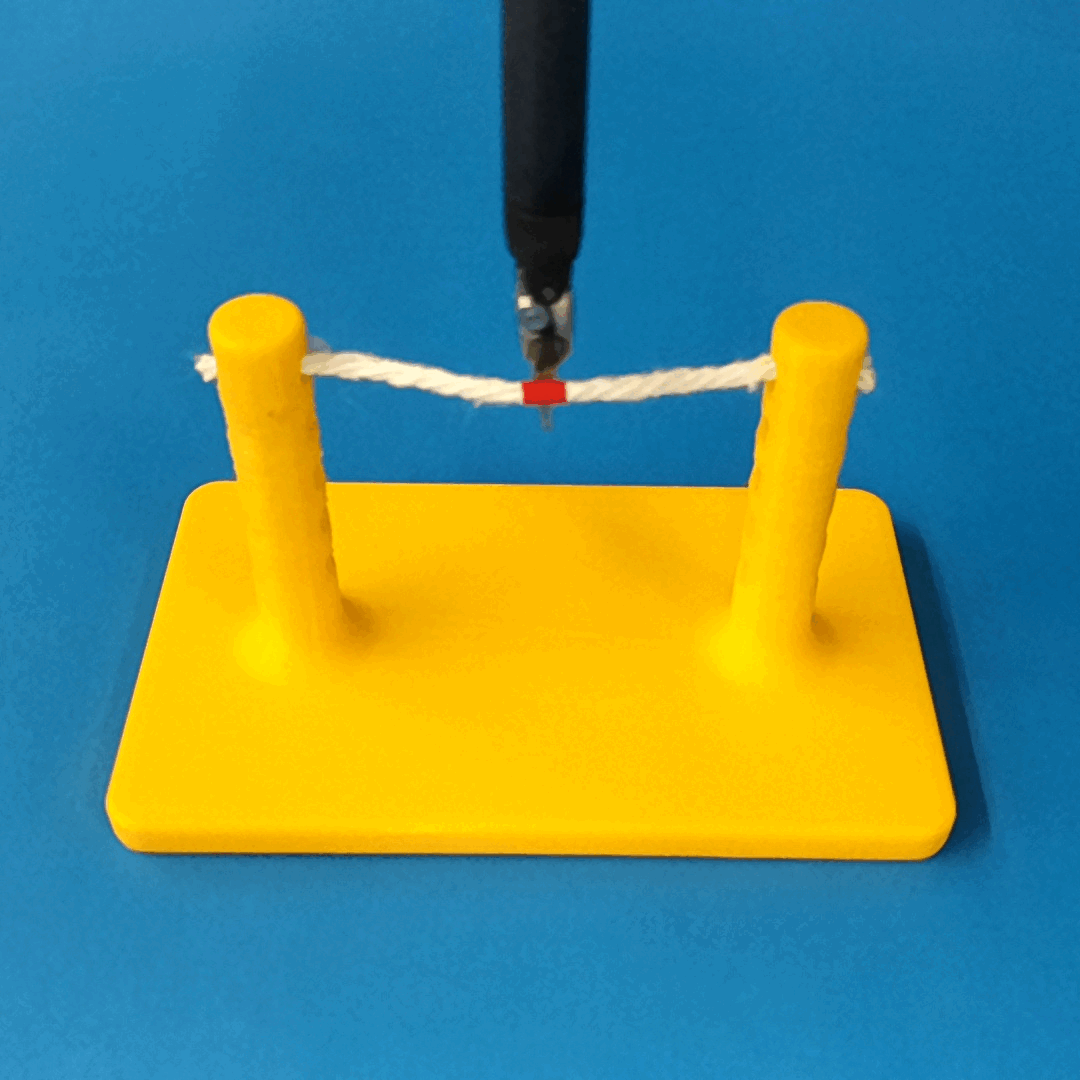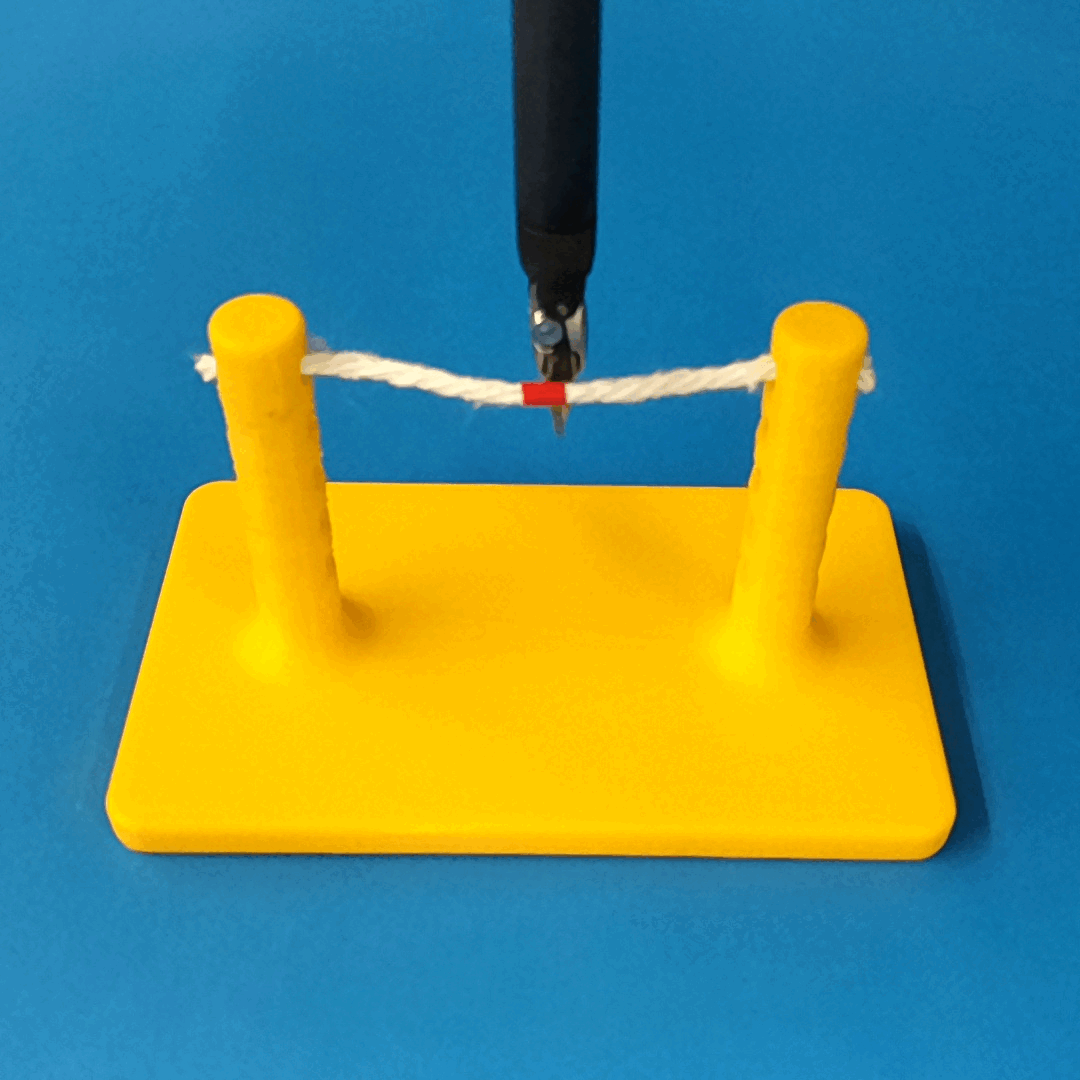
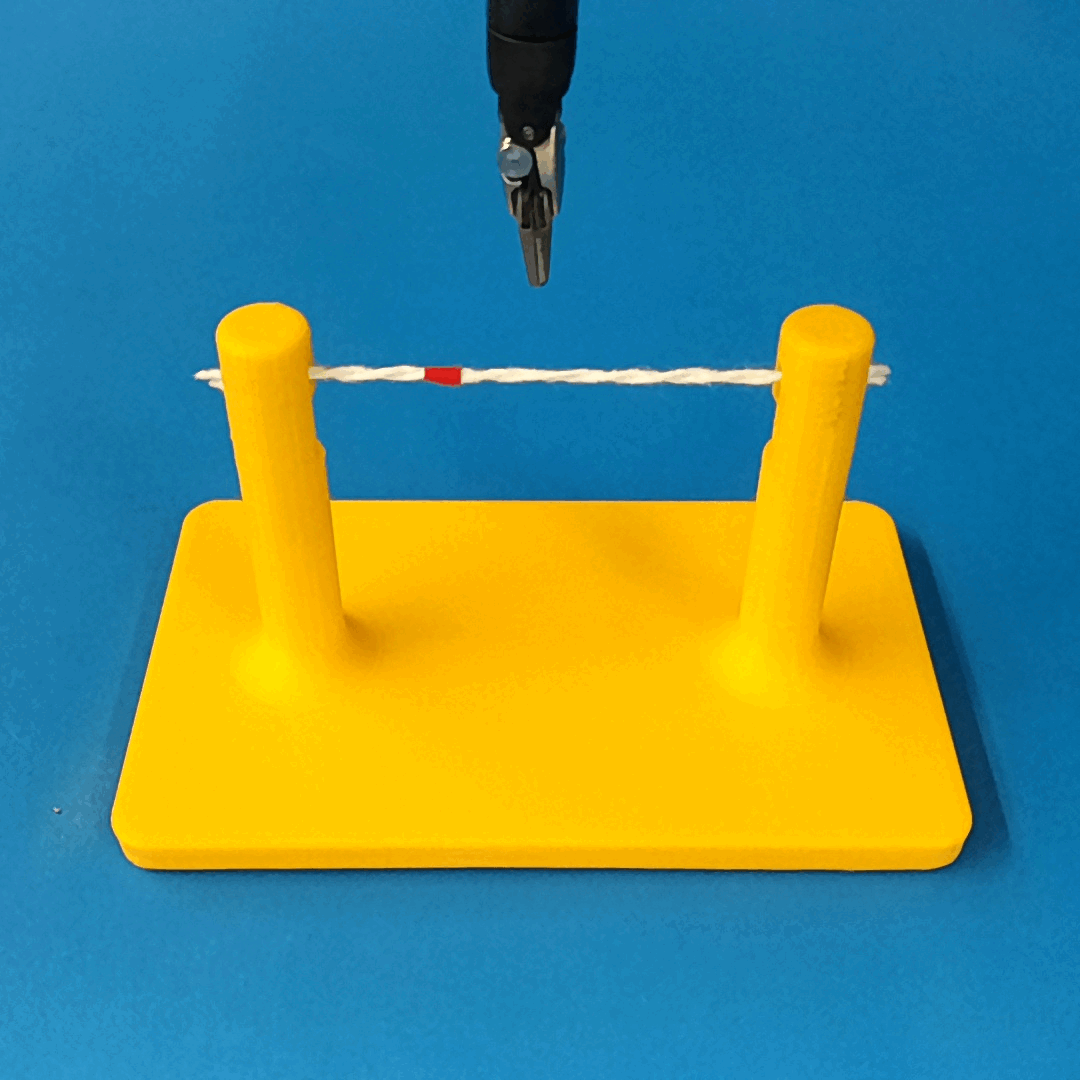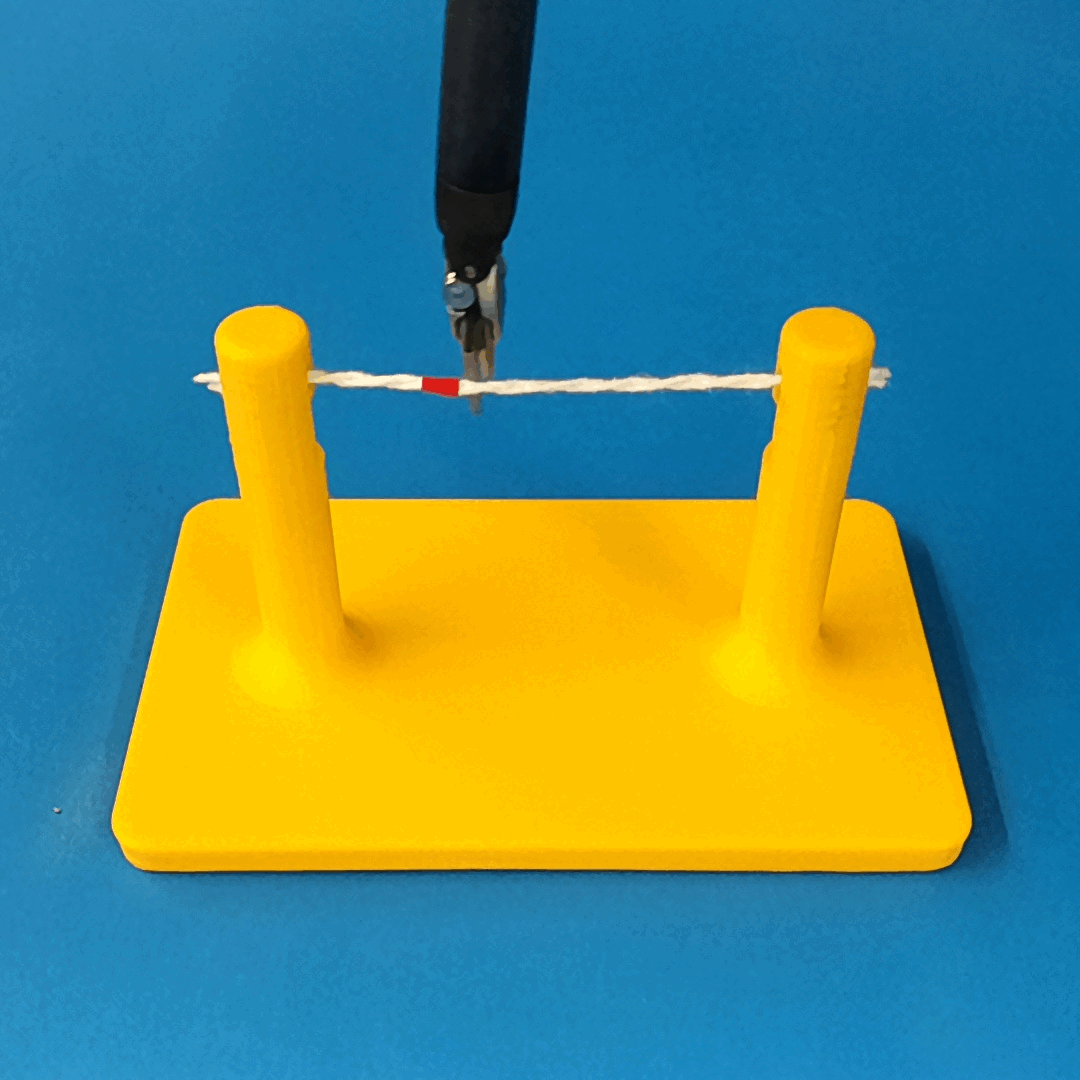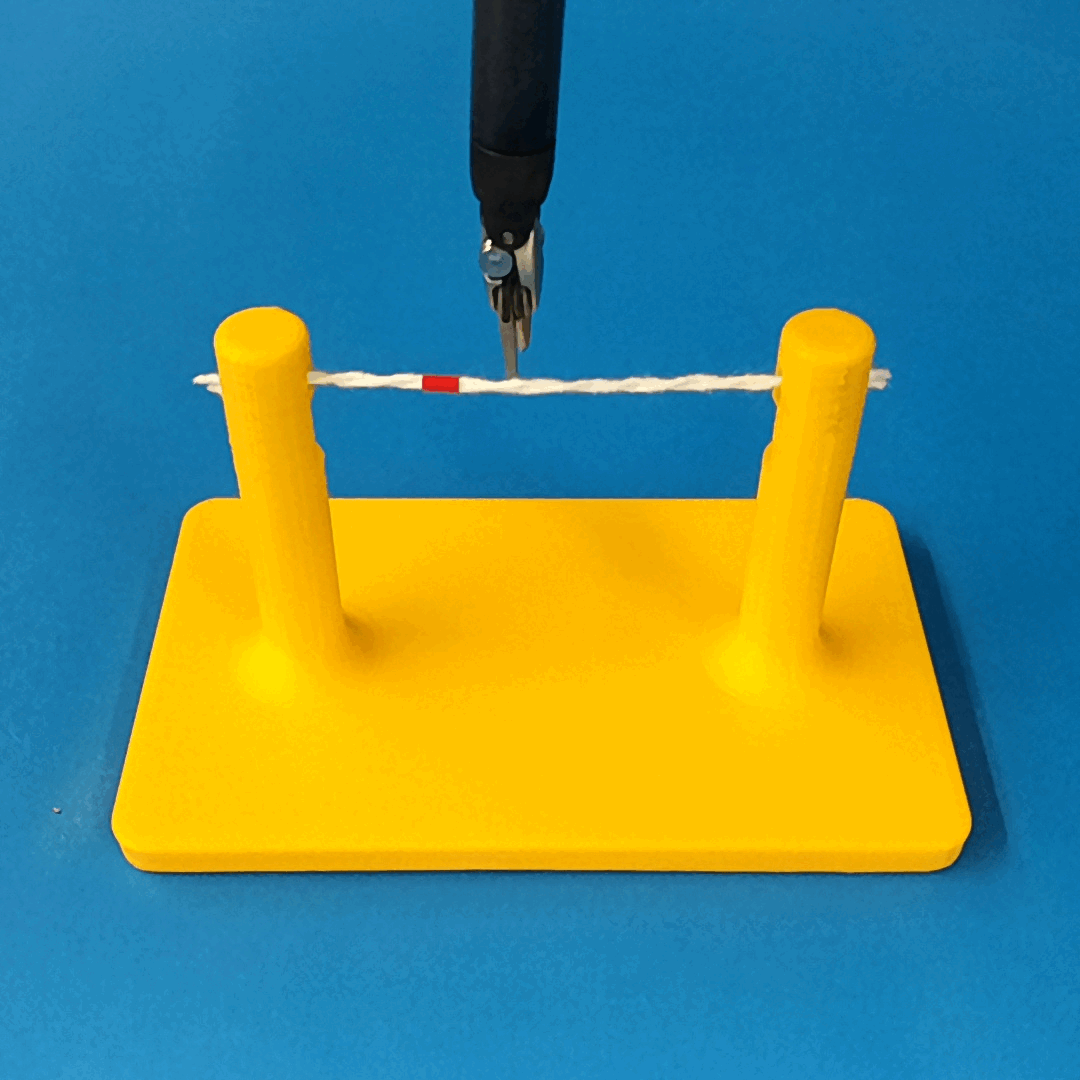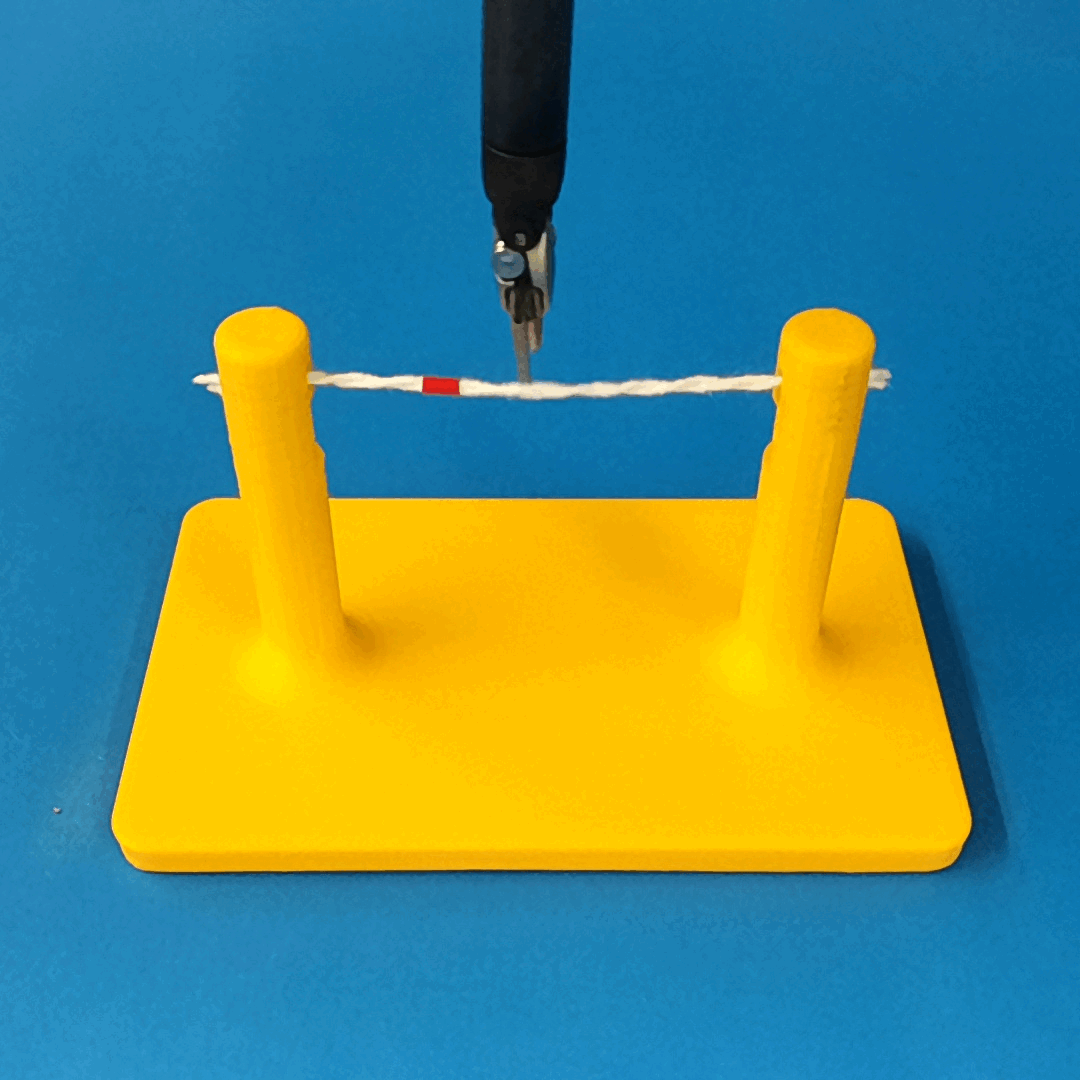
Overview of Methods
We build a simulation for cutting using Round Tip Scissors with contact collisions and cutting physics, and train vision-based agents to solve a rope cutting task.
Scissors (RTS) Modeling

Particle Physics
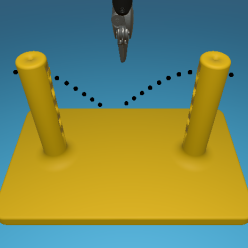
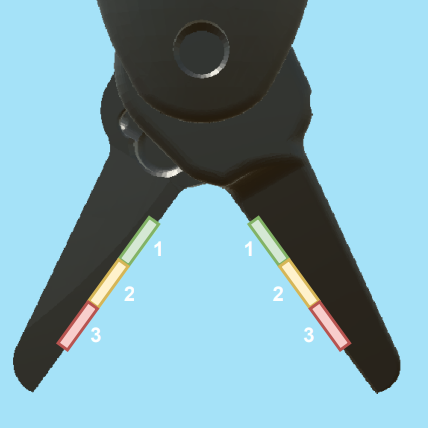
Reward Shaping
Sim2Real Transfer
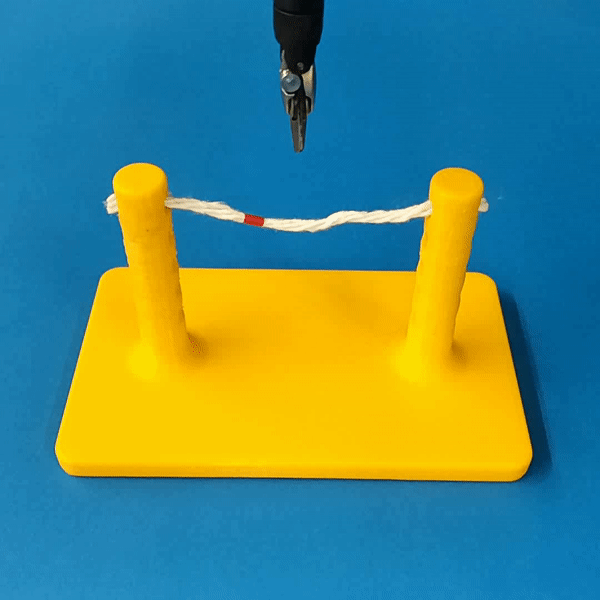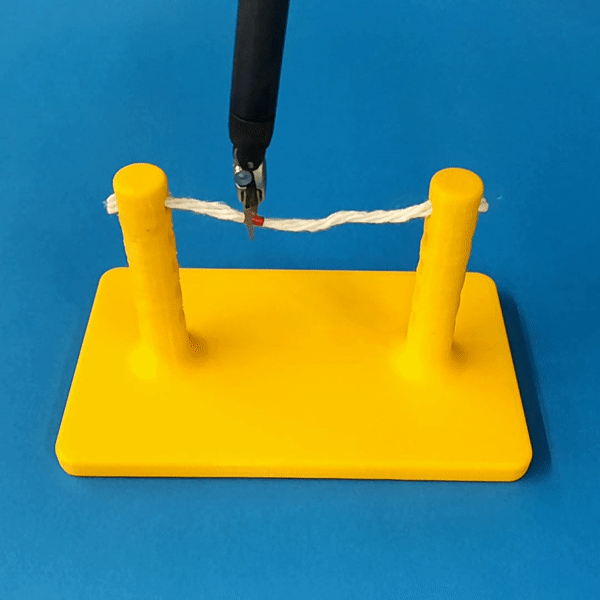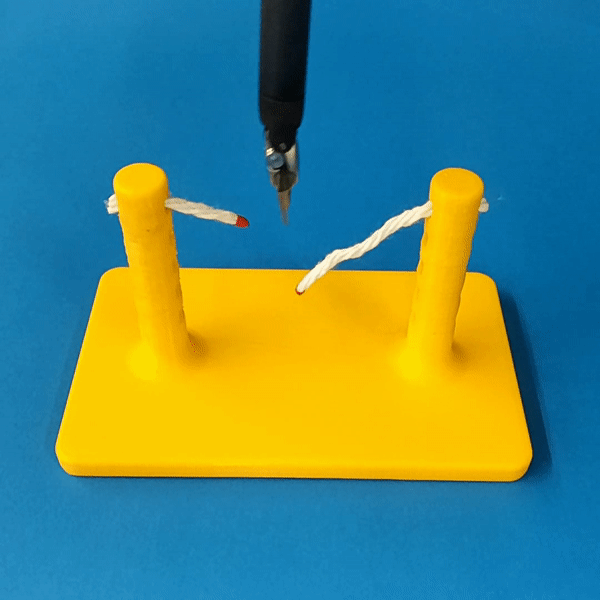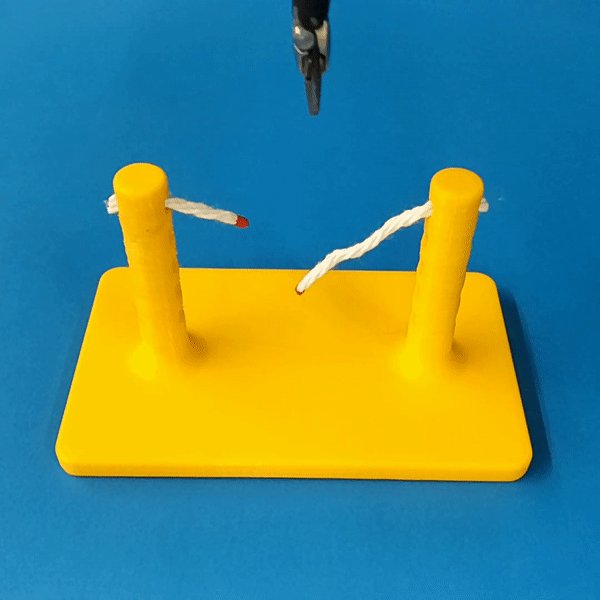
The simulation models typical collision contact and cutting contacts.
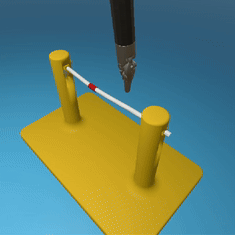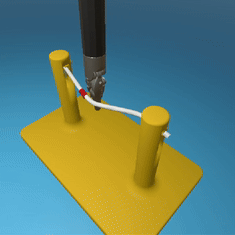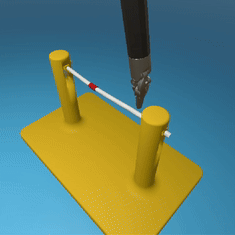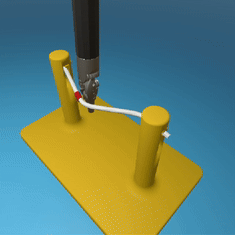
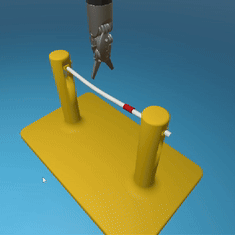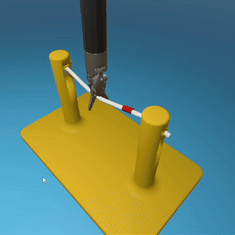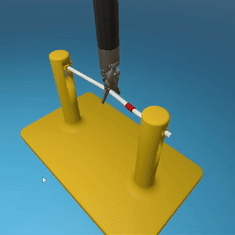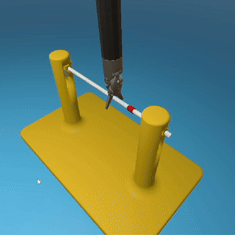
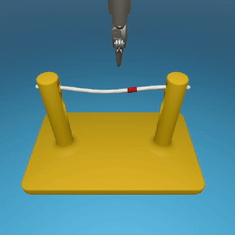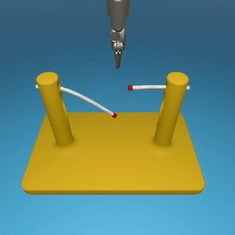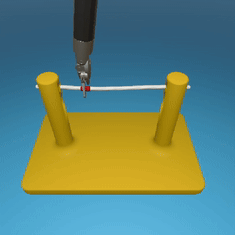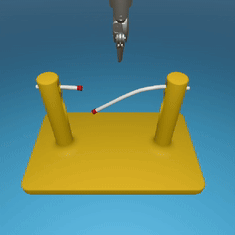
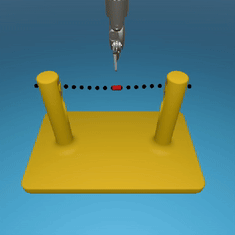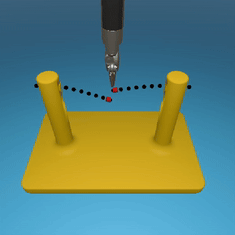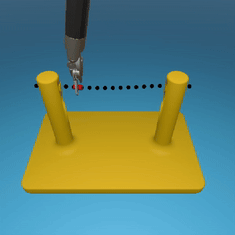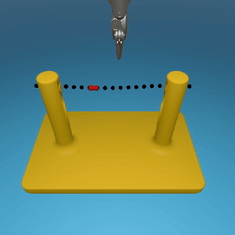
MedRCT Framework
Our Sim2Real pipeline builds off our concurrent work MedRCT, a modular robotics teleoperative control framework. Using MedRCT, we can easily swap between simulation and real components at any step, providing easy and seamless sim2real testing and execution.

Results
Our results show robust policy transfer from simulation.
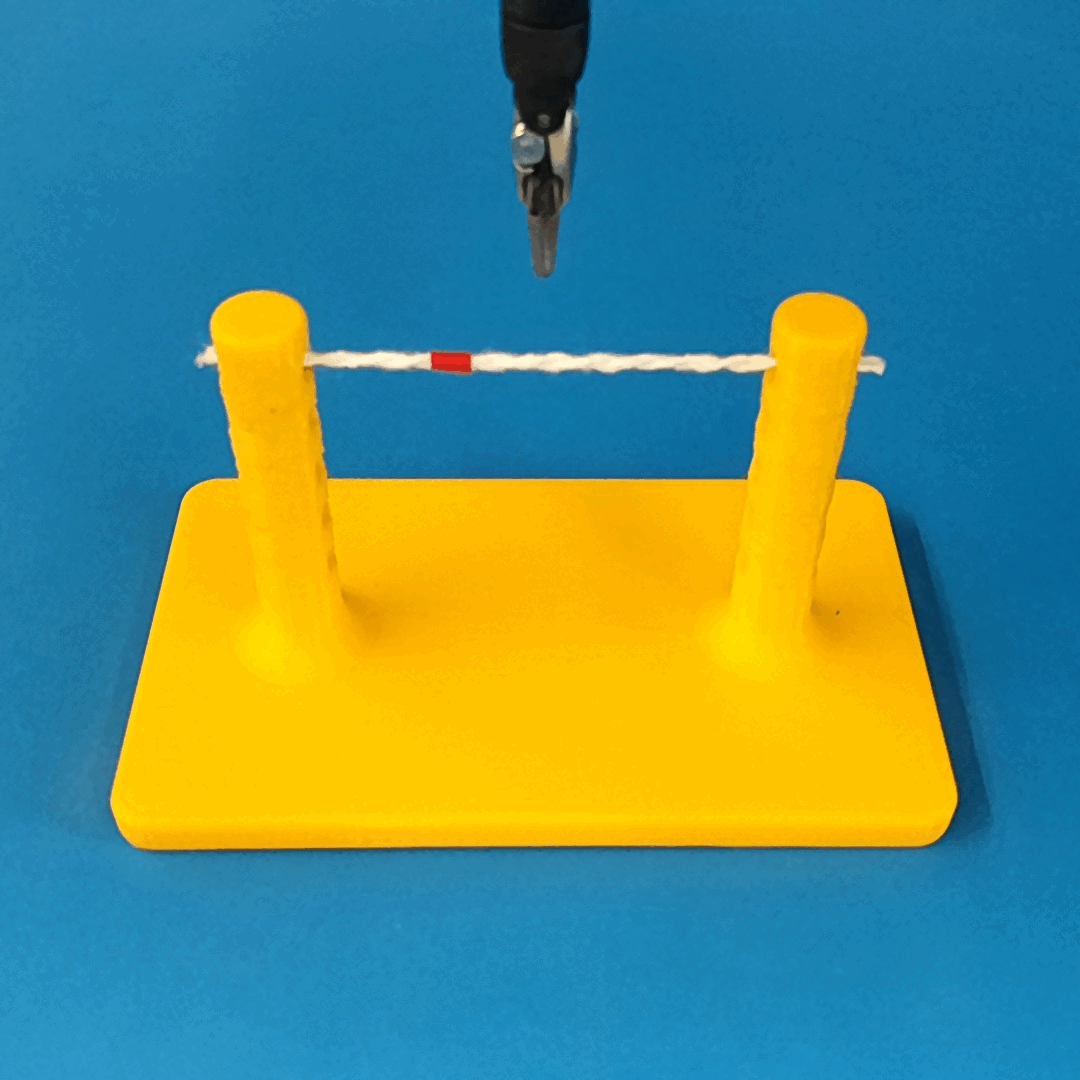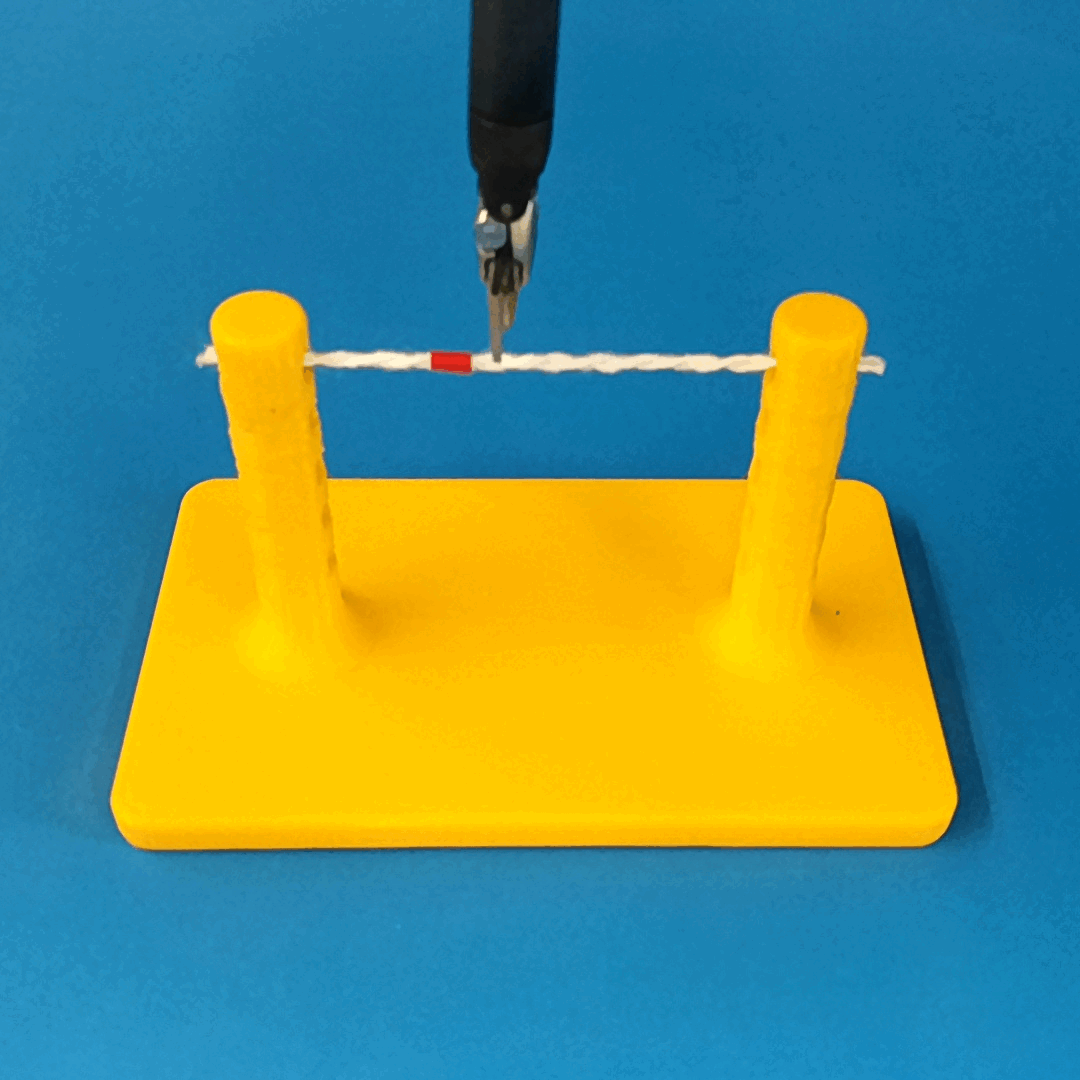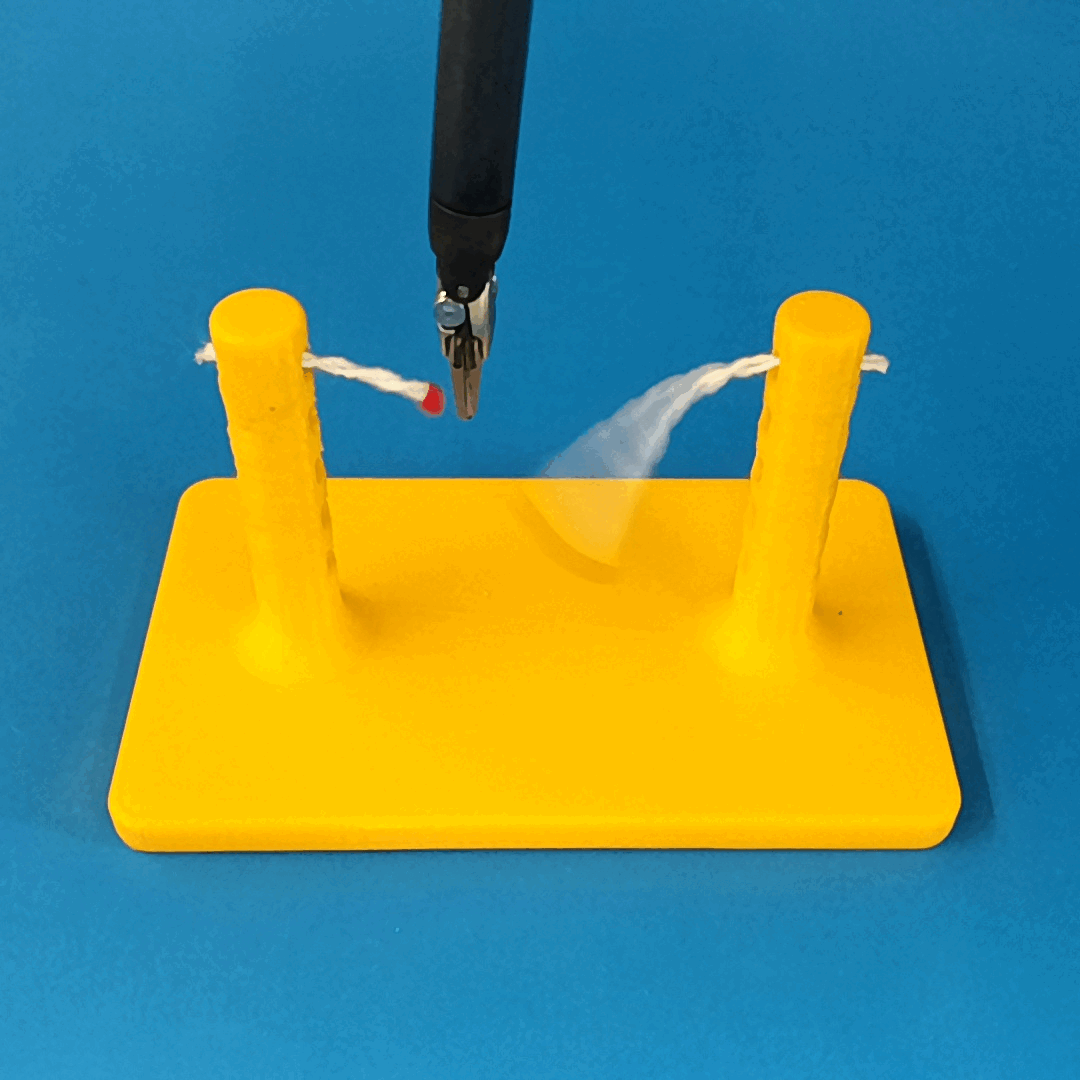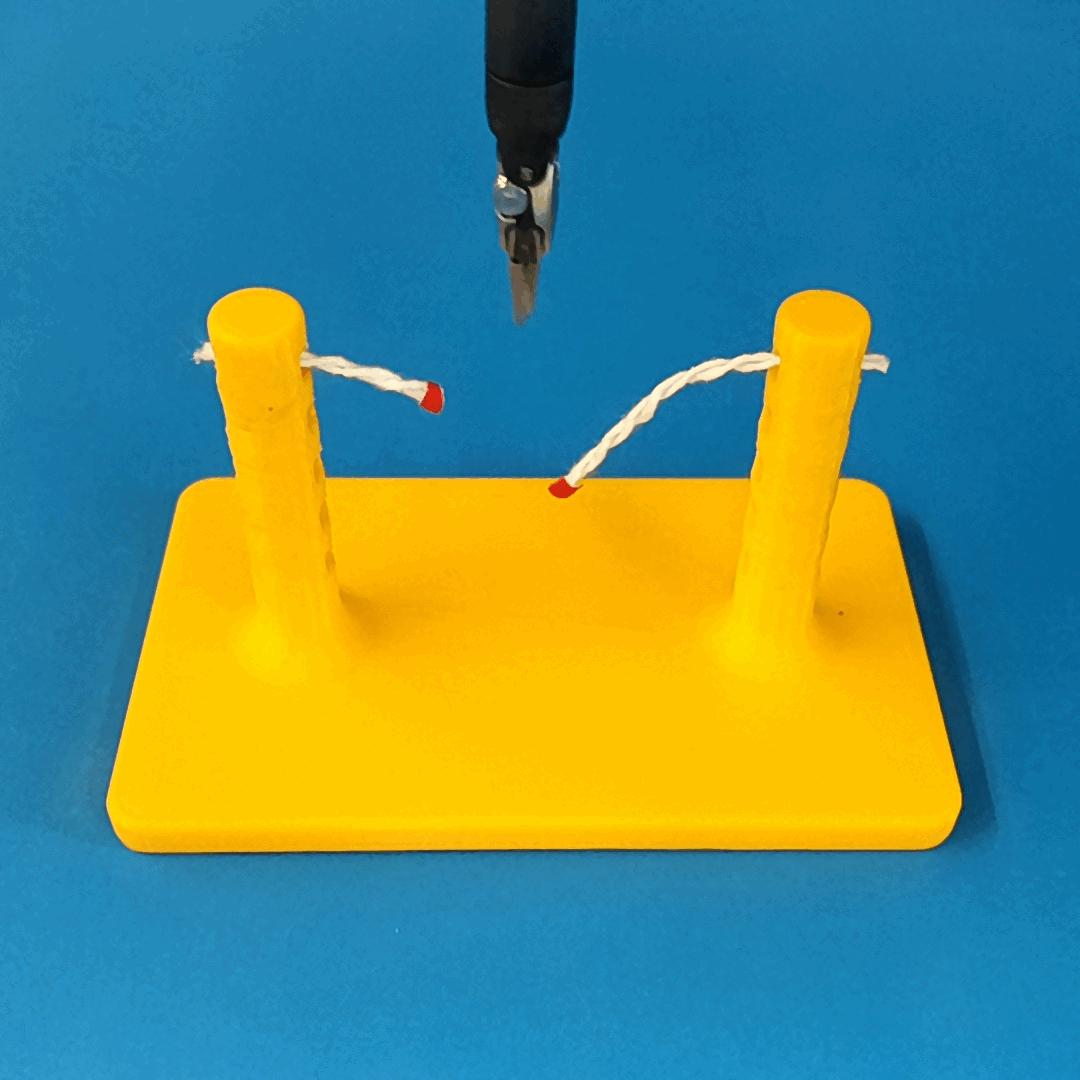
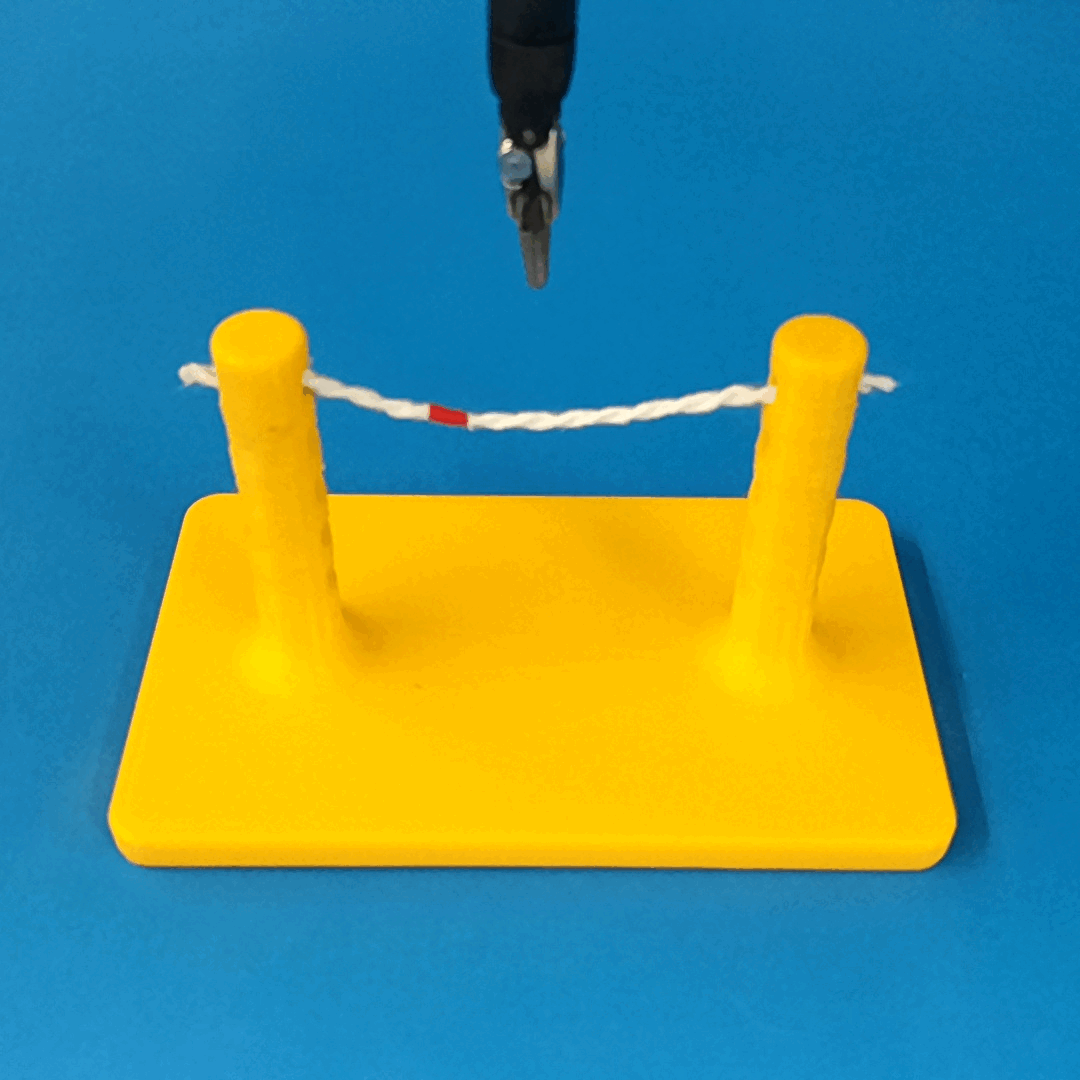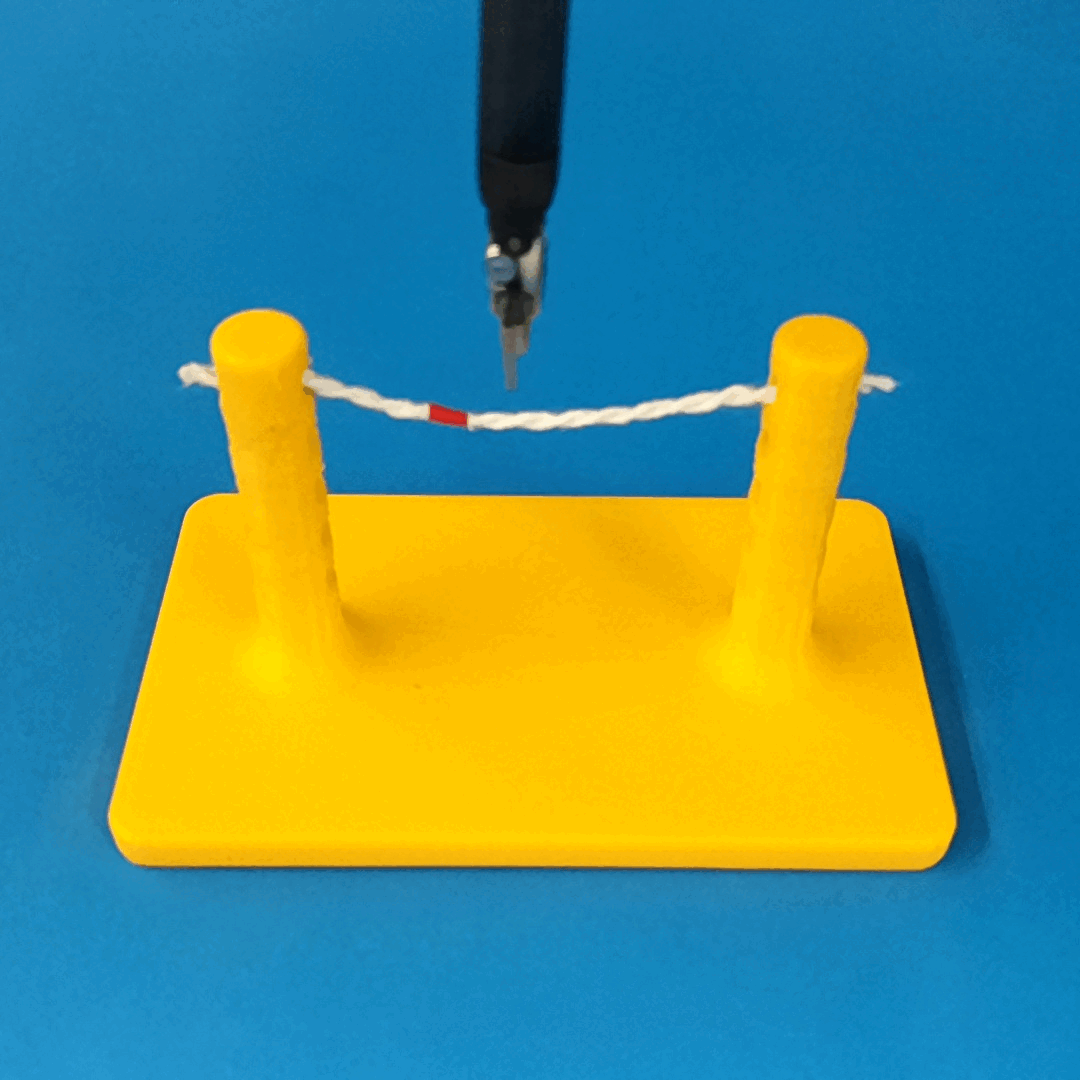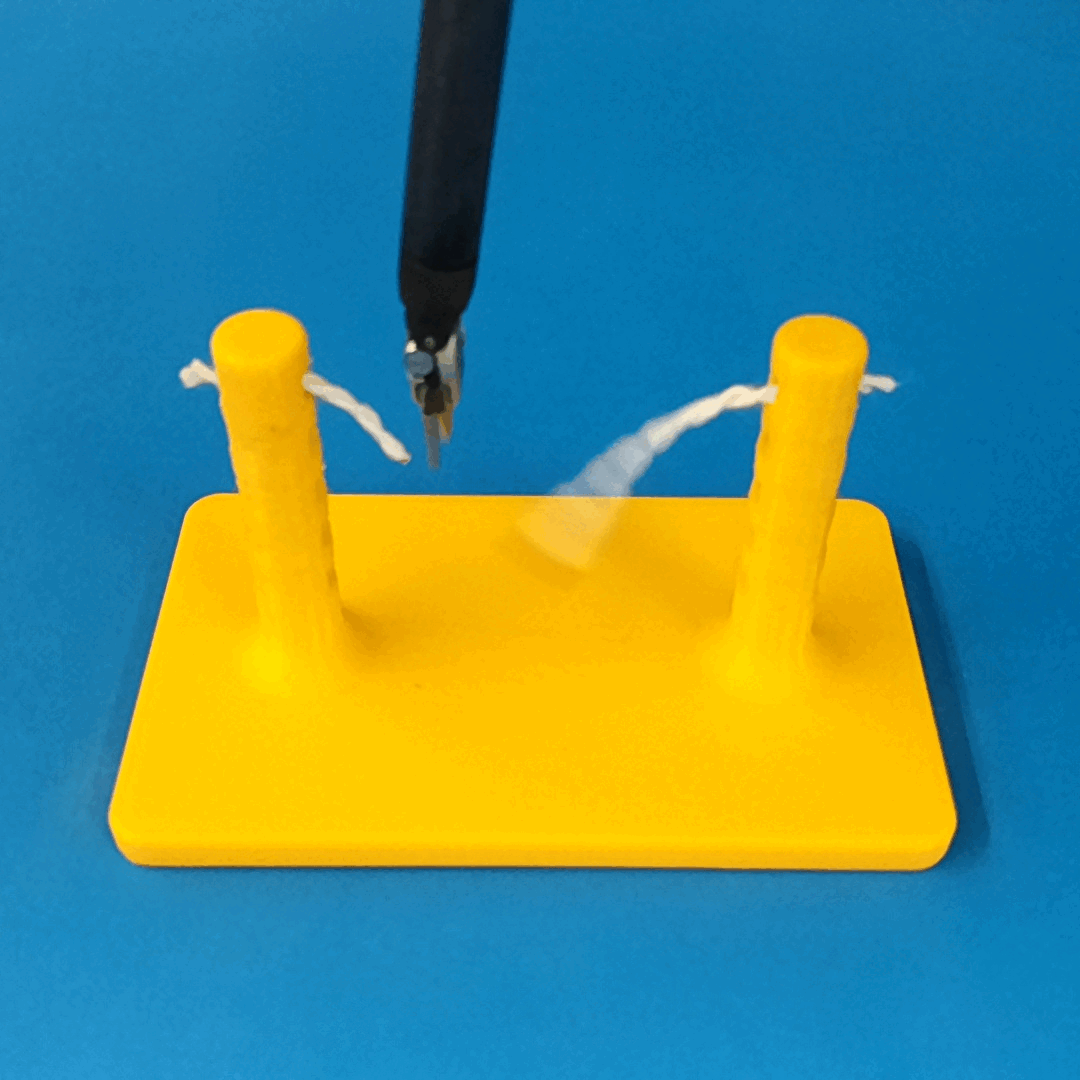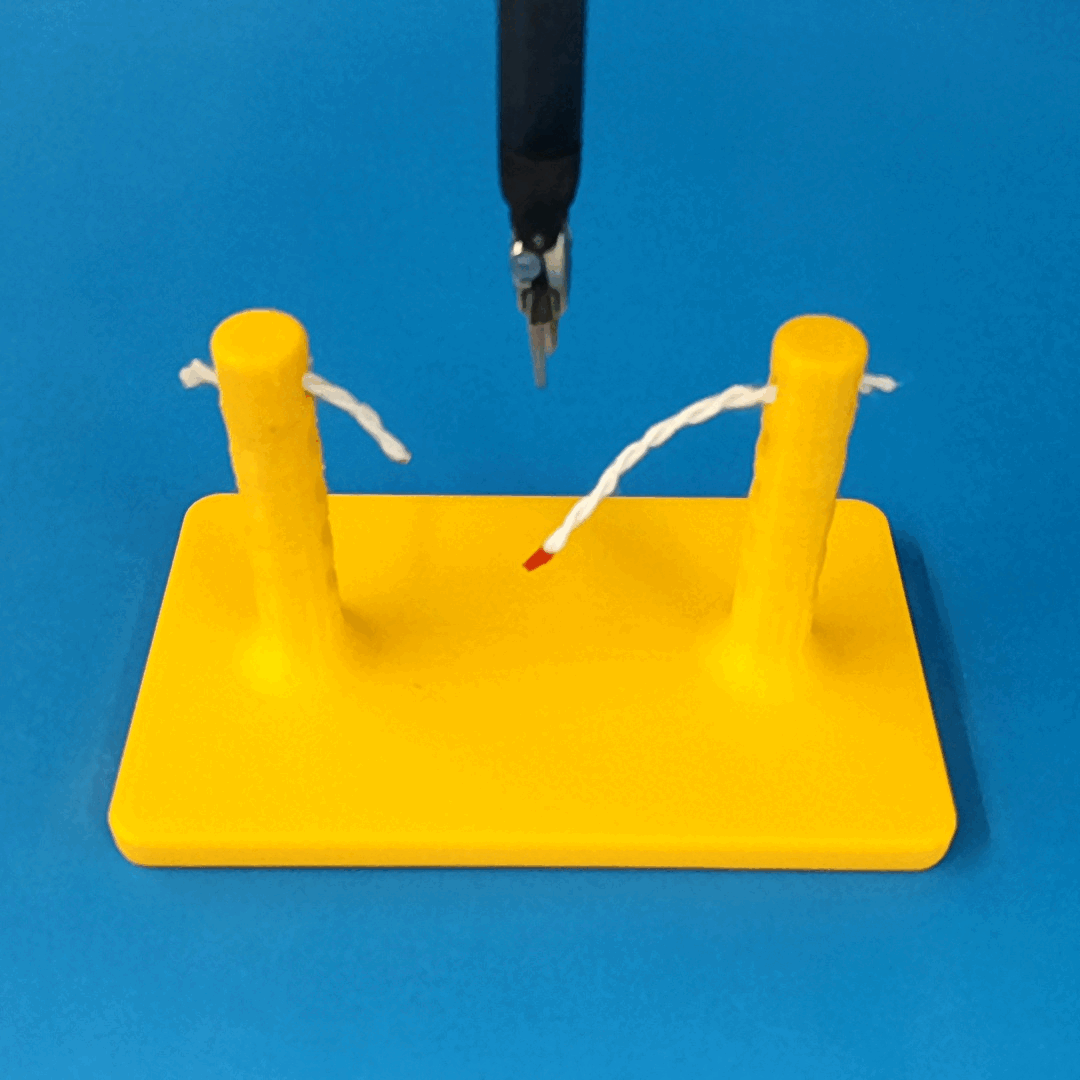
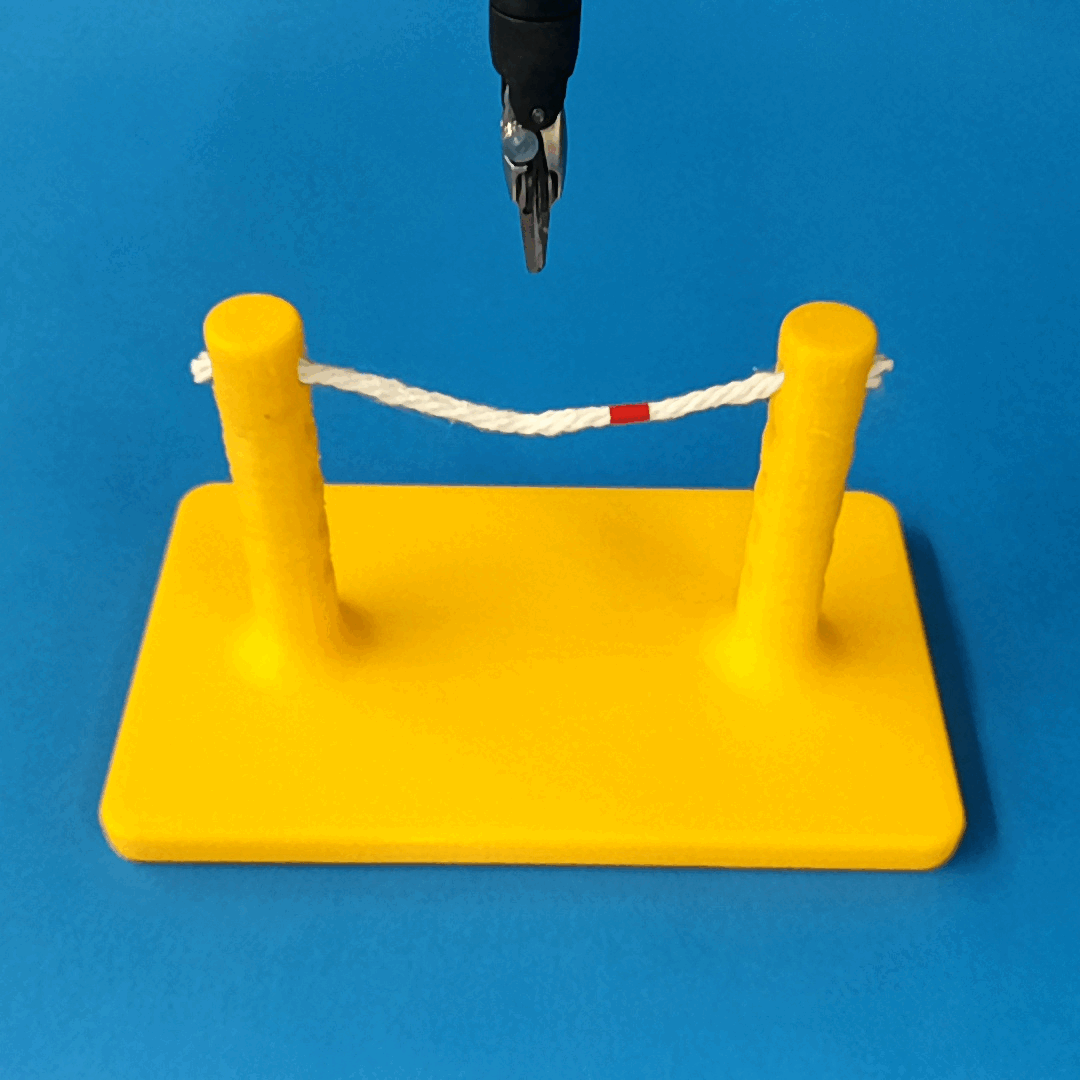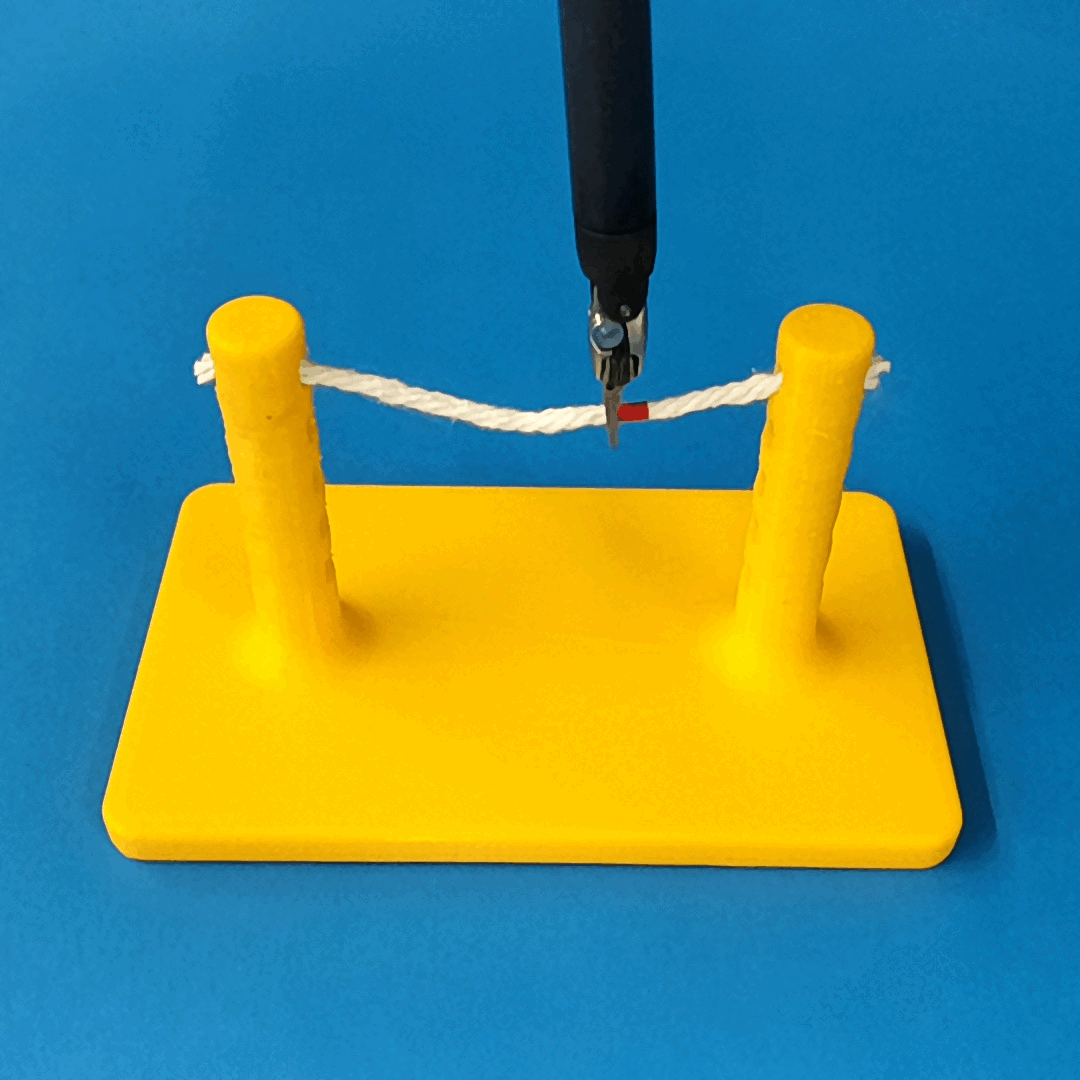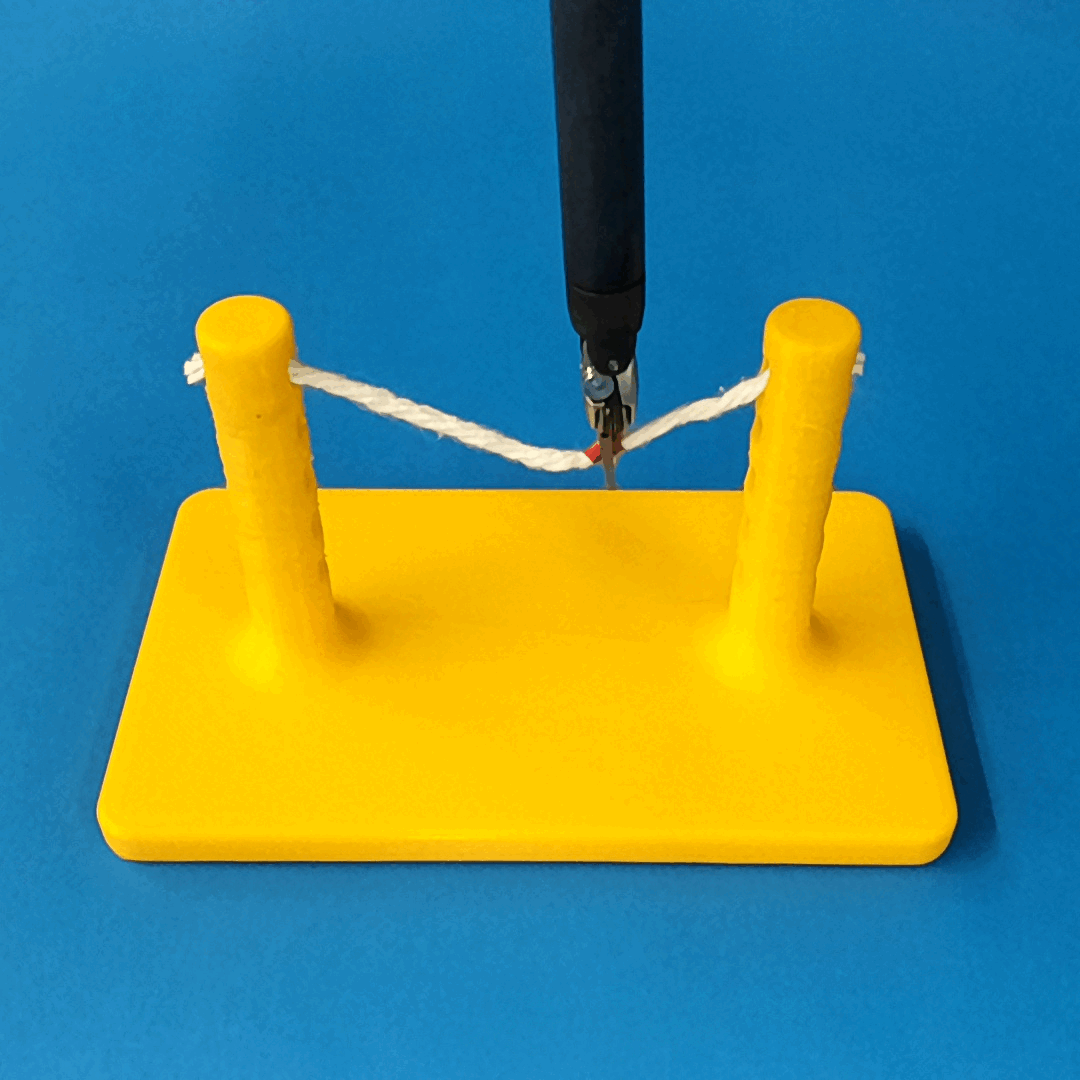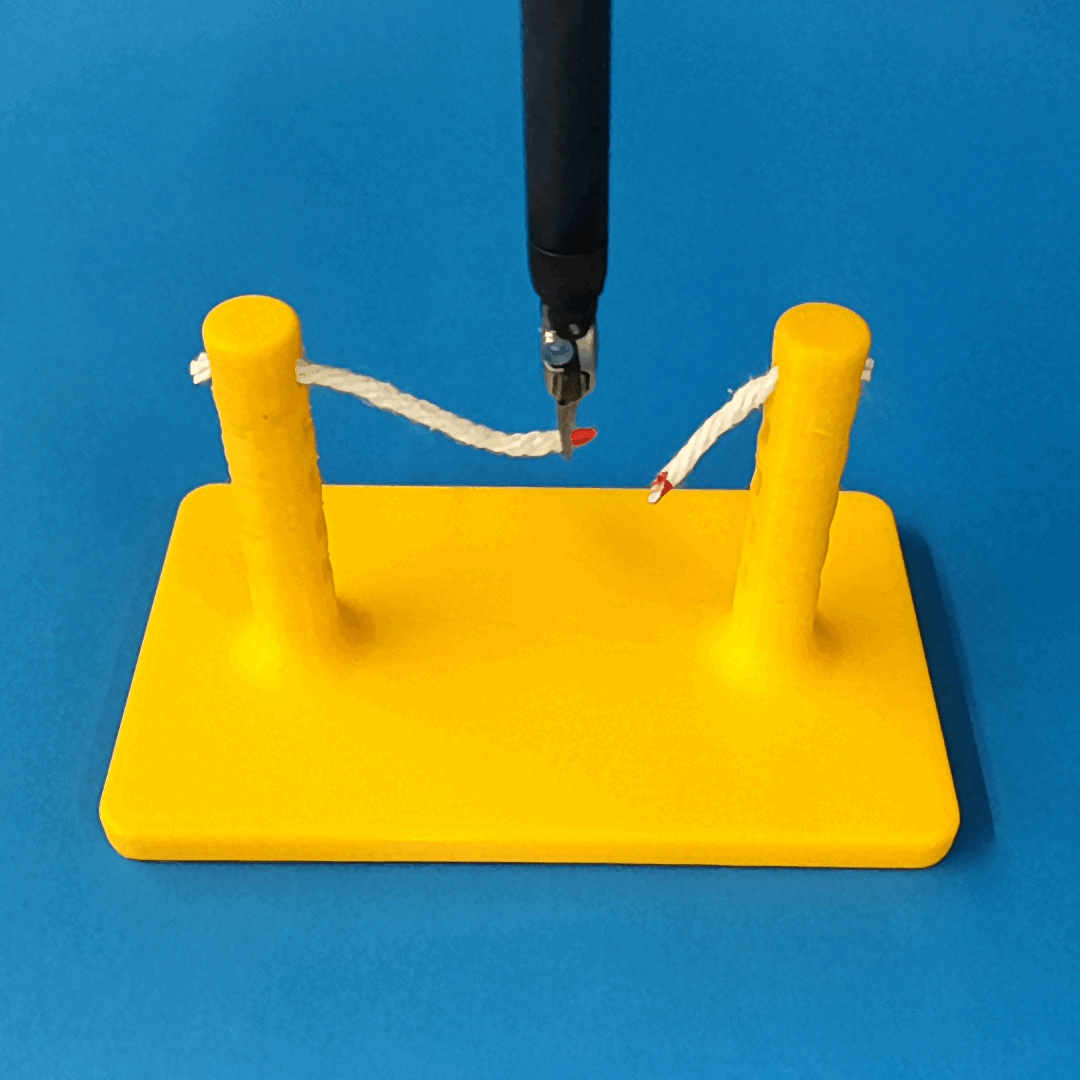
Robust Policy

The vision-based policy is robust to real-time changes of the environment. The camera and lighting can be moved during executions and the policy will still cut. By formulating the problem as visual servoing, and applying enough domain randomization, even extreme changes will not effect the policy

BibTeX Citation
@article{haiderbhai2024cutrope, author = {Haiderbhai, Mustafa and Gondokaryono, Radian and Wu, Andrew and Kahrs, Lueder A.}, title = {Sim2Real Rope Cutting with a Surgical Robot Using Vision-based Reinforcement Learning}, journal = {Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1109/TASE.2024.3410297},}
